What Does Choline Do For The Body?
Important research regarding choline and its benefits came to light in the late 1930s, when scientists and medical researchers uncovered a substance within pancreatic tissue that was able to prevent fat from accumulating in the liver. Subsequent studies concluded that, in addition to being found in the pancreas and liver, choline is actually a component that exists in nearly every human cell. Choline has a number of important roles in the body.
Significance
Significance
Choline is an organic vitamin-like nutrient that aids the body in creating a number of important substances and compounds. Choline is regularly classified within the B vitamin family because it has similar traits and operates in conjunction with them. The Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine noted choline's importance in 1998 and categorized it as a vital nutrient.
Features
Features
Choline is categorized as a lipotropic, indicating that it works by helping the liver rid fat, which is later used by the body for additional energy. Choline also supports the liver's overall function by transmitting the lipids to ensure the liver holds on to surplus fats and cholesterol that can harm our bodies. By assisting in the production of lipotropic agents that are able to reduce the amount of carbohydrates transformed into fat and promote the body's manufacturing of good cholesterol, choline plays a significant role in boosting the health and function of the bladder, kidneys, liver and pancreas.
Function
Function
Choline plays a critical role in our overall health and maintenance, as it holds antioxidant properties that support the development, healing and preservation of our glands, organs, bodily tissue and other systems. Furthermore, choline manufactures phosphatidylcholines, a class of phospholipids that is vital to the preservation and health of cell membranes.
Benefits
Benefits
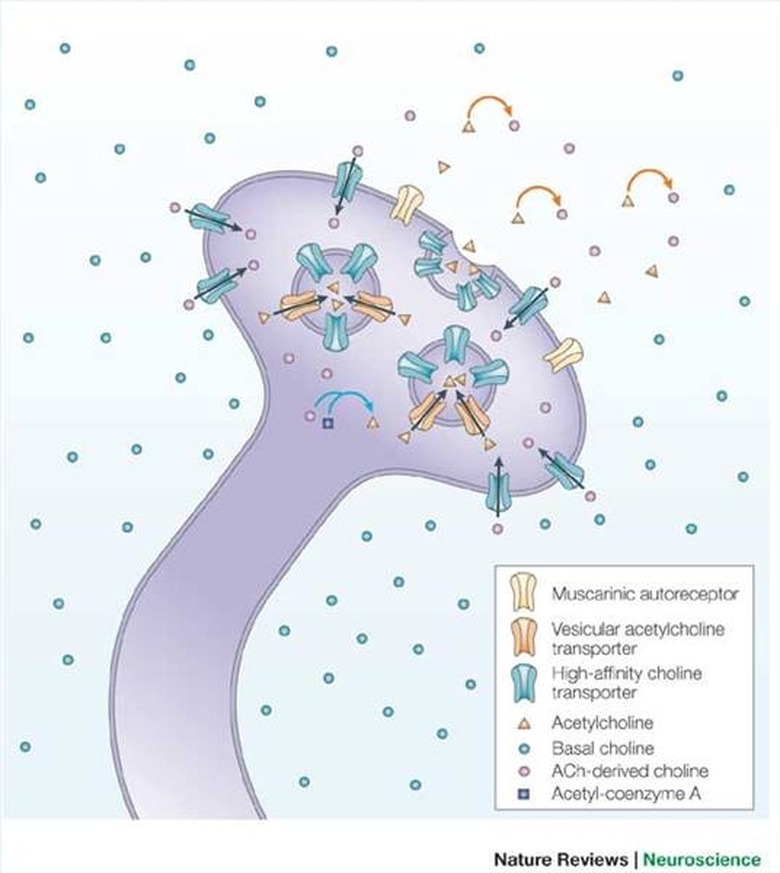
Choline also enhances different brain and nerve functions by generating the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, along with other vital compounds that the body makes and are critical to the health of cell membranes. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine assists with the conduction of impulses that occur between neurons. Acetylcholine is continually produced and broken down by our bodies and is considered to have an effect on things like appetite, behavior, memory, mood, muscle control, muscle movement and sleep.
Considerations
Considerations
The human body manufactures a certain amount choline naturally; it can also be found in foods such as:
- beef
- cod fish
- salmon
- shrimp
- eggs
- milk
- peanuts
- wheat germ
- various vegetables
- dietary supplements
Because this micronutrient boasts numerous health benefits, it's important that a person intake an adequate amount. According to the Food and Nutrition Board at the Institute of Medicine of the National Academy of Sciences, the adequate amount ranges from 425 and 550 mg daily. The body's ability to ingest and distribute choline tends to decline with age. Because it's so important for the function and configuration of nerves, choline levels should be monitored.
Cite This Article
MLA
Spinello, Serena. "What Does Choline Do For The Body?" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/choline-body-5105652/. 24 April 2017.
APA
Spinello, Serena. (2017, April 24). What Does Choline Do For The Body?. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/choline-body-5105652/
Chicago
Spinello, Serena. What Does Choline Do For The Body? last modified August 30, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/choline-body-5105652/