Definition Of Molecular Bonds
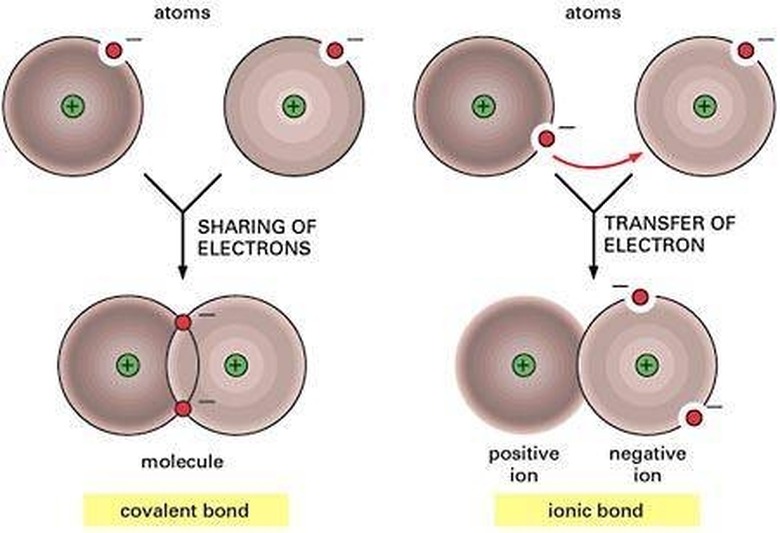
A molecular, or covalent bond, is formed when atoms bond by sharing pairs of electrons. This sharing can occur from atom to atom, or from an atom to another molecular bond.
Types
Types
The are two types of molecular bonds: polar bonds and non-polar bonds. In polar bonds, the molecular bond is unevenly shared between atoms; in non-polar bonds, the electrons are evenly shared between the two atoms.
Features
Features
Molecular bonds are classified as either singular bonds or multiple bonds. Molecular bonds form single bonds, where two atoms only share one pair of electrons.
Multiple Molecular Bonds
Multiple Molecular Bonds
The double bond consists of two pairs of electrons, a triple bond consists of three pairs and quadruple bonds share four pairs of electrons; there are quintuple and sextuple bonds as well.
Coordinate Covalent Bond
Coordinate Covalent Bond
In a coordinate covalent bond, a covalent, or molecular bond, is formed when only one of the two atoms is responsible for providing both electrons.
Disulfide Bond
Disulfide Bond
A disulfide bond is a molecular bond that is formed when two sulfide atoms are linked to form polypeptide chains in proteins.
High Energy Bonds
High Energy Bonds
High energy bonds release high energy levels when the bond undergoes hydrolysis.
Ionic Bonds
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds cause the transfer of electrons from one atom to another atom, leaving it with a negative charge.
Cite This Article
MLA
Manal, Naima. "Definition Of Molecular Bonds" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/facts-4909878-definition-molecular-bonds/. 9 January 2018.
APA
Manal, Naima. (2018, January 9). Definition Of Molecular Bonds. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/facts-4909878-definition-molecular-bonds/
Chicago
Manal, Naima. Definition Of Molecular Bonds last modified August 30, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/facts-4909878-definition-molecular-bonds/