What Are The Functions Of A Zener Diode?
Zener diodes are silicon diodes specifically constructed to operate in what is known as the breakdown region. For this reason, they are also referred to as voltage-regulator diodes.
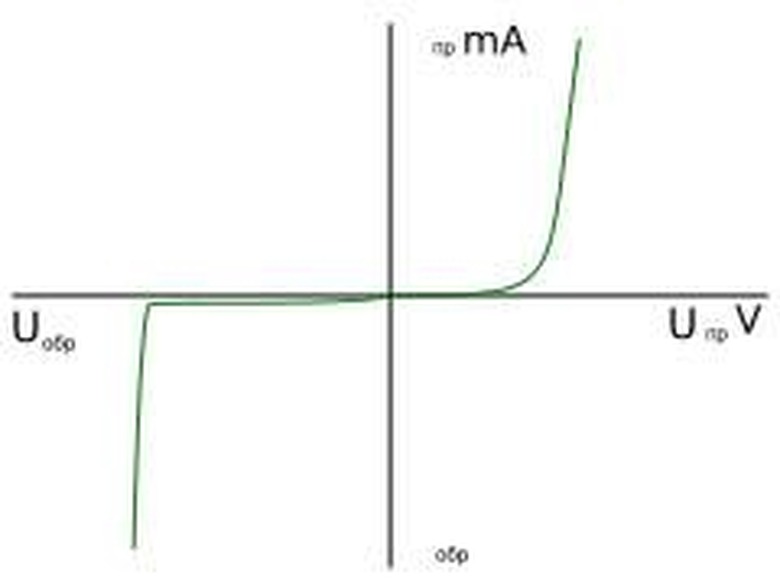
Breakdown Voltage
Breakdown Voltage
The maximum voltage rating specifies how much reverse voltage a diode can withstand before breakdown occurs. For most, this is at least 50 V. Ordinary diodes that are reverse-biased have reverse current that is so small as to be zero, so that the diode behaves similar to an open circuit. When the maximum voltage rating is exceeded, however, a large reverse current is produced, and the diode becomes destroyed. This destruction occurs at what is known as the reverse breakdown voltage or peak inverse voltage (PIV). Zener diodes are created to operate optimally when they are reverse-biased and, instead of being destroyed, will conduct electricity under conditions where normal a diode's breakdown voltages are reached. Zener diode breakdown voltages can range from 2 to 200 V.
Significance
Significance
The diodes are able to maintain constant output voltages throughout current changes in the circuit, thus stabilizing the voltage under different loads. They are therefore most often used as voltage regulators for low current circuits. They can protect circuits from voltage spikes or overloads or static electricity. Zener diodes are also often used to generate reference voltages for amplifier circuits.
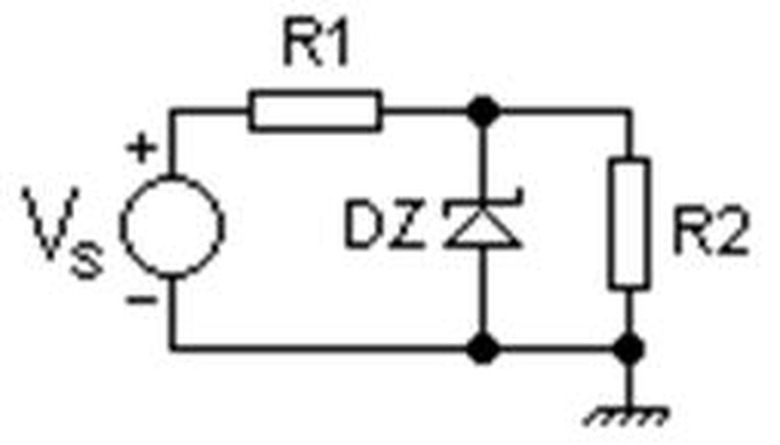
Operation
Operation
For voltage regulation, Zener diodes are placed into circuits in a reverse-biased position parallel to the load, as shown.
Uses
Uses
Zener diodes are found in devices such as power supplies and surge protectors.
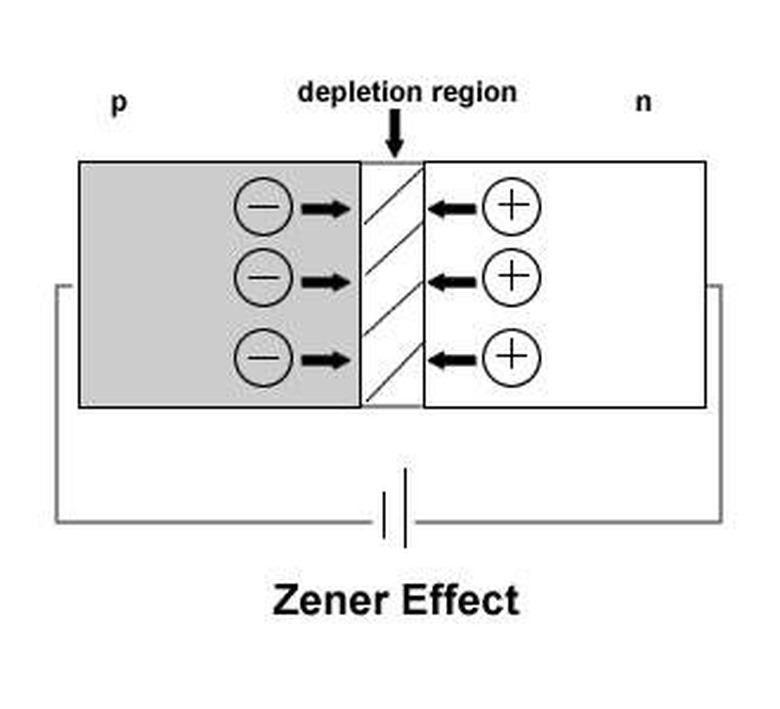
Expert Insight
Expert Insight
The diodes operate on what is known as the Zener Effect. The p-n junction is heavily doped, which causes it to become narrow and obtain an intense electric field. When reverse biased, this intense electric field causes ionization where electrons are pulled away from their valence orbits, so that they become free and can flow.
Cite This Article
MLA
Lewis, Kim. "What Are The Functions Of A Zener Diode?" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/functions-zener-diode-5094948/. 24 April 2017.
APA
Lewis, Kim. (2017, April 24). What Are The Functions Of A Zener Diode?. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/functions-zener-diode-5094948/
Chicago
Lewis, Kim. What Are The Functions Of A Zener Diode? last modified March 24, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/functions-zener-diode-5094948/