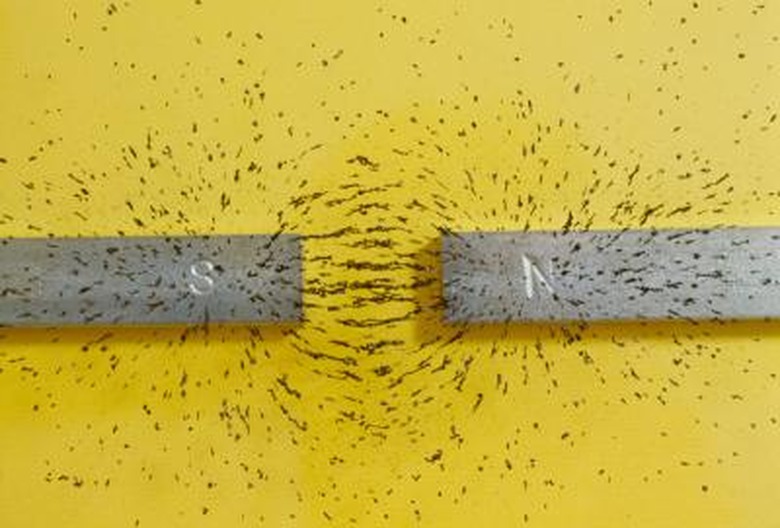
How Does Heat Affect Magnets?
Magnetic materials should maintain a balance between temperature and magnetic domains (the atoms' inclination to spin in a certain direction). When exposed to extreme temperatures, however, this balance is destabilized; magnetic properties are then affected. While cold strengthens magnets, heat can result in the loss of magnetic properties. In other words, too much heat can completely ruin a magnet.
How it Works
How it Works
Excessive heat causes atoms to move more rapidly, disturbing the magnetic domains. As the atoms are sped up, the percentage of magnetic domains spinning in the same direction decreases. This lack of cohesion weakens the magnetic force and eventually demagnetizes it entirely.
In contrast, when a magnet is exposed to extreme cold, the atoms slow down so the magnetic domains are aligned and, in turn, strengthened.
Ferromagnetism
Ferromagnetism
The way in which specific materials form permanent magnets or interact strongly with magnets. Most everyday magnets are a product of ferromagnetism.
Paramagnetism
Paramagnetism
A type of magnetism that occurs only in the presence of an external magnetic field. They are attracted to magnetic fields, but they are not magnetized when the external field is removed. That's because the atoms spin in random directions; the spins aren't aligned, and the total magnetization is zero.
Aluminum and oxygen are two examples of materials that are paramagnetic at room temperature.
Curie Temperature
Curie Temperature
Named for the French physicist Pierre Curie, the Curie Temperature is the temperature at which no magnetic domain can exist because the atoms are too frantic to maintain aligned spins. At this temperature, the ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic. Even if you cool the magnet, once it has become demagnetized, it will not become magnetized again. Different magnetic materials have different Curie Temperatures, but the average is about 600 to 800 degrees Celsius.
Cite This Article
MLA
Arana, Whitney. "How Does Heat Affect Magnets?" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/heat-affect-magnets-4926450/. 24 April 2017.
APA
Arana, Whitney. (2017, April 24). How Does Heat Affect Magnets?. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/heat-affect-magnets-4926450/
Chicago
Arana, Whitney. How Does Heat Affect Magnets? last modified March 24, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/heat-affect-magnets-4926450/