How Do Plants Make Their Own Food?
What do plants eat? Although you hear talk about "feeding" plants when fertilizing them, this isn't really the same thing as when humans or other animals eat. Plants make their own food through a biochemical process called oxygenic photosynthesis. With access to just sunlight, water and carbon dioxide, plants can produce their own fuel – and as a byproduct of photosynthesis, trees and other plants release oxygen, which is essential for the survival of other life forms on Earth.
What Is Photosynthesis?
What Is Photosynthesis?
Plants are autotrophs, which means that they are organisms that make their own food, notes the Smithsonian Science Education Center. Plants make their own food using photosynthesis, a process that originated over three billion years ago, according to PennState.
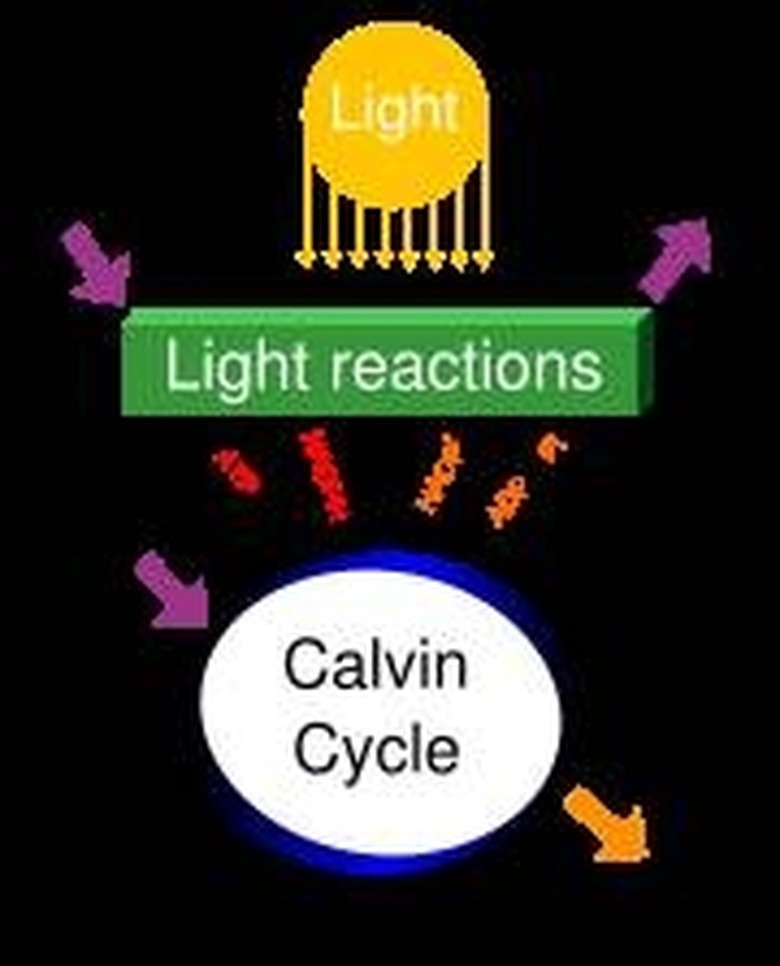
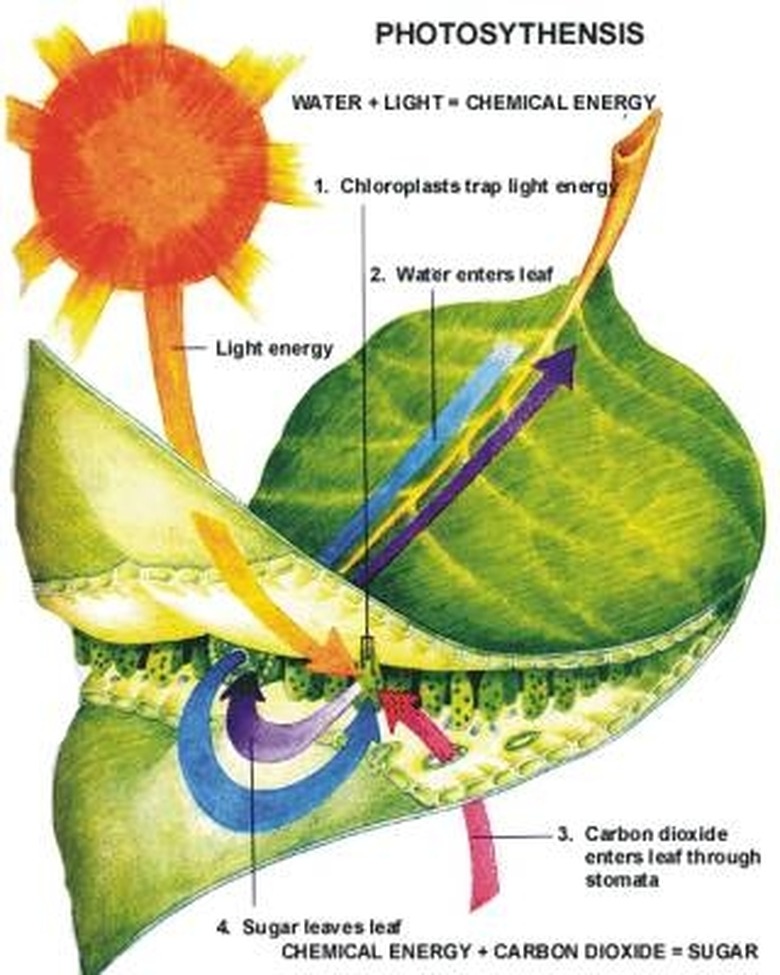
Basically, plants use energy from sunlight to split the hydrogen and oxygen in water molecules, or H2O. Then, they combine the hydrogen and oxygen with CO2, or carbon dioxide, to make carbohydrates. These carbohydrates, or sugars, are used by plants as "food," allowing them to live, grow and reproduce.
Here is the basic formula for oxygenic photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
All plants, algae and cyanobacteria – also known as blue-green algae – use oxygenic photosynthesis to feed themselves. This process occurs within chloroplasts, which are parts of plant cells that contain chlorophyll, the pigment that gives plants their green color.
There are also bacterial organisms that make their own food through a method of photosynthesis does not produce oxygen, which is called anoxygenic photosynthesis. Anoxygenic photosynthesis does not require water, and pigments called bacteriochlorophylls are used to absorb light instead of chlorophylls.
Chlorophyll and Chloroplasts
Chlorophyll and Chloroplasts
During oxygenic photosynthesis, chlorophyll, a green pigment found in chloroplasts, absorbs energy in the form of red and blue lightwaves from the sun. This solar energy is essential for the process of photosynthesis, which happens within special structures in plant cells called chloroplasts.
The chlorophyll in plant cells gives plant leaves their green color, and photosynthesis only occurs in the green parts of plants. Plant roots and tree trunks are not green because they are not photosynthetic.
The non-photosynthetic parts of plants, like roots, need energy to grow, too. Since these parts can't make their own food, plants move the carbohydrates produced by their leaves through veins and other vascular tissues to feed the non-green parts of their structures.
There are some plants with non-green leaves, like red maples. The leaves of these plants also contain chlorophyll, and these plants are photosynthetic; but high levels of a pigment called anthocyanin simply overpower the green color of the chlorophyll in species with non-green leaves, sometimes giving them a red or purple hue.
Byproducts of Photosynthesis
Byproducts of Photosynthesis
Plants are essential to all life – in more ways than one. These amazing green life forms capture energy from the sun not only to feed themselves but also to feed people! Many basic foods, like fruits, vegetables, bread and grains, are plant products. And the meat and dairy foods people eat are produced by animals that eat plants.
Humans can't make their own food like plants can, so humans rely on plants to convert sunlight into energy people can consume in the form of the foods that they eat. All human food, whether plant- or animal-based, starts with a photosynthetic organism.
Along with providing food for humans, plants also take carbon dioxide out of the air and release oxygen into the environment. By replenishing the oxygen in the air, plants make it possible for humans and other animals to live on Earth. As a byproduct of making their own food, plants make the planet habitable for other life forms – which is one of the reasons that photosynthesis is one of the most important processes in the solar system.
Cite This Article
MLA
Sloane, Christina. "How Do Plants Make Their Own Food?" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/how-do-plants-make-their-own-food-12146332/. 30 September 2021.
APA
Sloane, Christina. (2021, September 30). How Do Plants Make Their Own Food?. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/how-do-plants-make-their-own-food-12146332/
Chicago
Sloane, Christina. How Do Plants Make Their Own Food? last modified August 30, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/how-do-plants-make-their-own-food-12146332/