Physical And Chemical Properties For The Element Aluminum
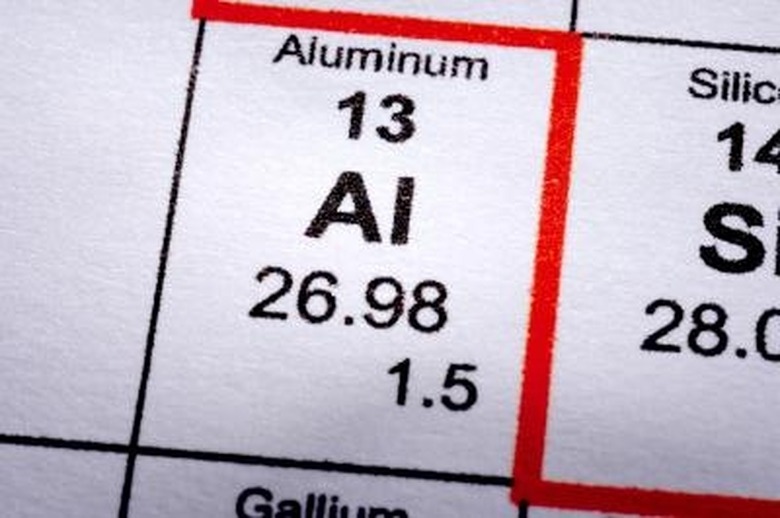
According to ChemistryExplained.com, "Aluminum is the third most abundant element on the Earth's crust." The first time that aluminum was isolated was in 1825 by Hans Christian Oersted. Aluminum has an atomic number of 13, and its atomic symbol is Al.
Physical Properties of Aluminum
Physical Properties of Aluminum
Aluminum is silvery-white in color. It melts at 1220.576 Fahrenheit and boils at 4472.33. Aluminum has an atomic weight of 26.98154, and an atomic radius of 143.1 pm. It is one of the most ductile and malleable metals. Aluminum is non-magnetic.
Chemical Properties of Aluminum
Chemical Properties of Aluminum
When it comes in contact with oxygen, aluminum forms an oxide skin called aluminum oxide. This skin helps to protect aluminum from corrosion. Aluminum catches fire easily if exposed to flame when it is in powdered form. It is also reactive with both acids and alkalis.
Uses of Aluminum
Uses of Aluminum
The physical and chemical properties of aluminum make it an ideal metal for making such products as culinary utensils, automotive parts, construction materials, and food and beverage containers.
Cite This Article
MLA
Lavoy, Desiree. "Physical And Chemical Properties For The Element Aluminum" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/physical-chemical-properties-aluminum-element-6785380/. 24 April 2017.
APA
Lavoy, Desiree. (2017, April 24). Physical And Chemical Properties For The Element Aluminum. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/physical-chemical-properties-aluminum-element-6785380/
Chicago
Lavoy, Desiree. Physical And Chemical Properties For The Element Aluminum last modified August 30, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/physical-chemical-properties-aluminum-element-6785380/