How To Find Relative Barometric Pressure
Absolute barometric pressure is the actual atmospheric air pressure at a particular location that profoundly depends upon the location altitude. Relative or sea level pressure is the corrected barometric pressure calculated for the sea or zero level, and usually used to refer atmospheric conditions. The importance of the relative pressure (P0) is that it allows calculating the absolute pressure (P) at any elevation (h) using the barometric formula: P=P0*exp(-Mgh/RT), where M molar mass of air, g standard gravity, T temperature and R universal gas constant. The relative barometric pressure is the pressure reported by weather stations.
Step 1
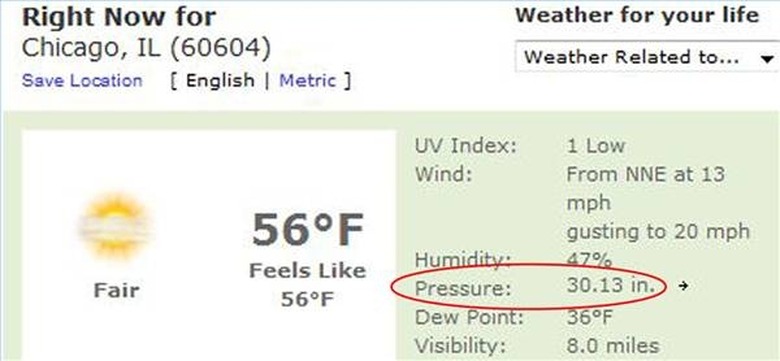
Navigate to the Weather Channel website (see Resources), and enter the location ZIP code in the field; click "Search."
Step 2
Read the relative barometric pressure (labeled "Pressure") in inches of mercury.
Step 3
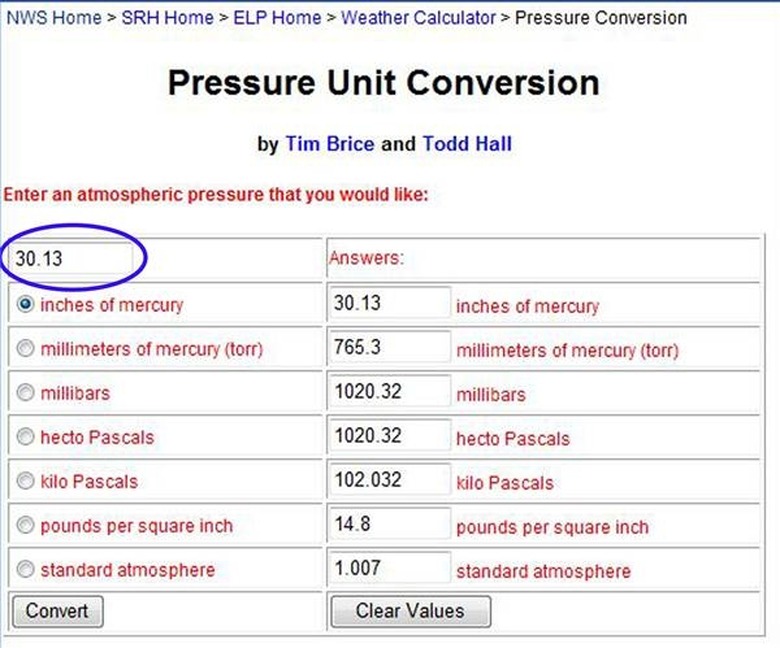
Navigate to the National Weather Service pressure unit converter (see Resources) to translate the pressure in inches of mercury to a different unit.
Step 4
Enter the pressure from Step 3 in the box, and select the "inches of mercury" radio button; click "Convert."
Step 5
Pressure values will be expressed in six different units.
Cite This Article
MLA
Contributor, . "How To Find Relative Barometric Pressure" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/relative-barometric-pressure-5075062/. 24 April 2017.
APA
Contributor, . (2017, April 24). How To Find Relative Barometric Pressure. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/relative-barometric-pressure-5075062/
Chicago
Contributor, . How To Find Relative Barometric Pressure last modified March 24, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/relative-barometric-pressure-5075062/