Science Facts About Magnets For Kids
A magnet is anything that creates a magnetic field, or exerts a force on ferromagnetic objects such as iron or other magnets. The Earth's magnetism comes from the large amount of liquid metal inside of the Earth's core.
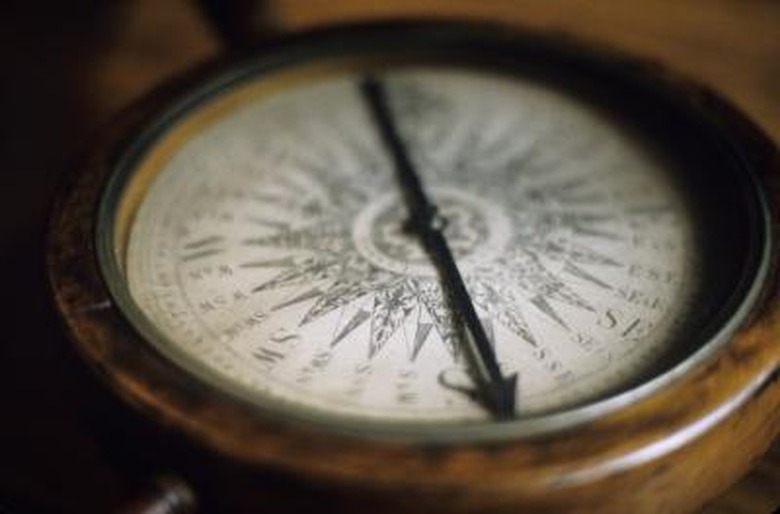
Lodestone
Lodestone
A lodestone, containing iron, is a magnet that naturally occurs in nature. It was used in ancient China and Greece to calibrate compasses. Sailors discovered that when a piece of magnetic material is suspended from a thread, it always points north-south.
Permanent vs. Induced
Permanent vs. Induced
Permanent magnets retain their charge forever, unless they are demagnetized. Induced magnets only become magnetized when they come in direct contact with a permanent magnet; they will lose their magnetism when no longer attached to a permanent magnet.
Magnetization
Magnetization
Hammering and heating a piece of metal in a north-south direction will align the atoms and magnetize the object. Rubbing a piece of ferromagnetic material in a north to south direction with another magnet can magnetize the object.
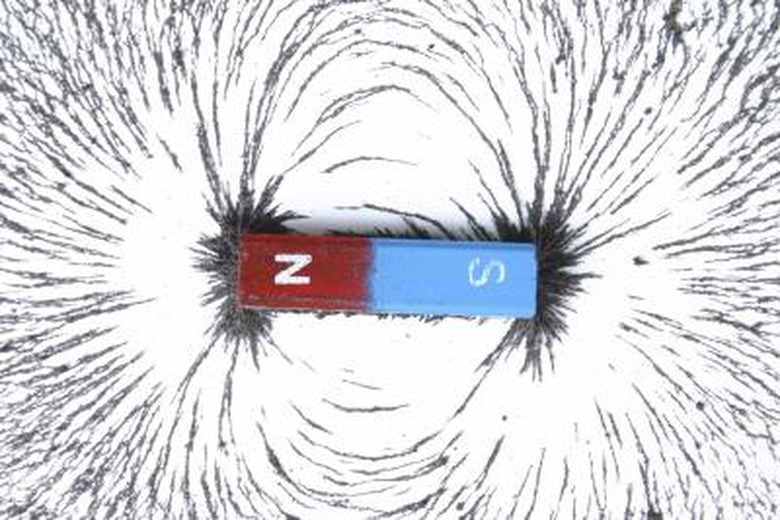
Opposites Attract
Opposites Attract
When the north pole of a magnet comes close to the north pole of another magnet, they will repel each other. When a north pole of a magnet comes into contact with the south pole of another magnet, they will attract each other.
De-magnetization
De-magnetization
When a magnet is heated in a hot flame, it will lose its magnetization because the molecules will become mixed up and no longer align in a north-to-south manner.
Cite This Article
MLA
Doc, Tommy. "Science Facts About Magnets For Kids" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/science-magnets-kids-5895999/. 24 April 2017.
APA
Doc, Tommy. (2017, April 24). Science Facts About Magnets For Kids. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/science-magnets-kids-5895999/
Chicago
Doc, Tommy. Science Facts About Magnets For Kids last modified August 30, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/science-magnets-kids-5895999/