What Are The Subunits Of DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic acid is present in the nucleus of every cell in our body in compactly folded up forms called chromosomes. The four building blocks that make up the DNA are repeated to form a long chain. They encode a vast amount of information, ranging from eye color to the predisposition to a disease.
Subunits of DNA
Subunits of DNA
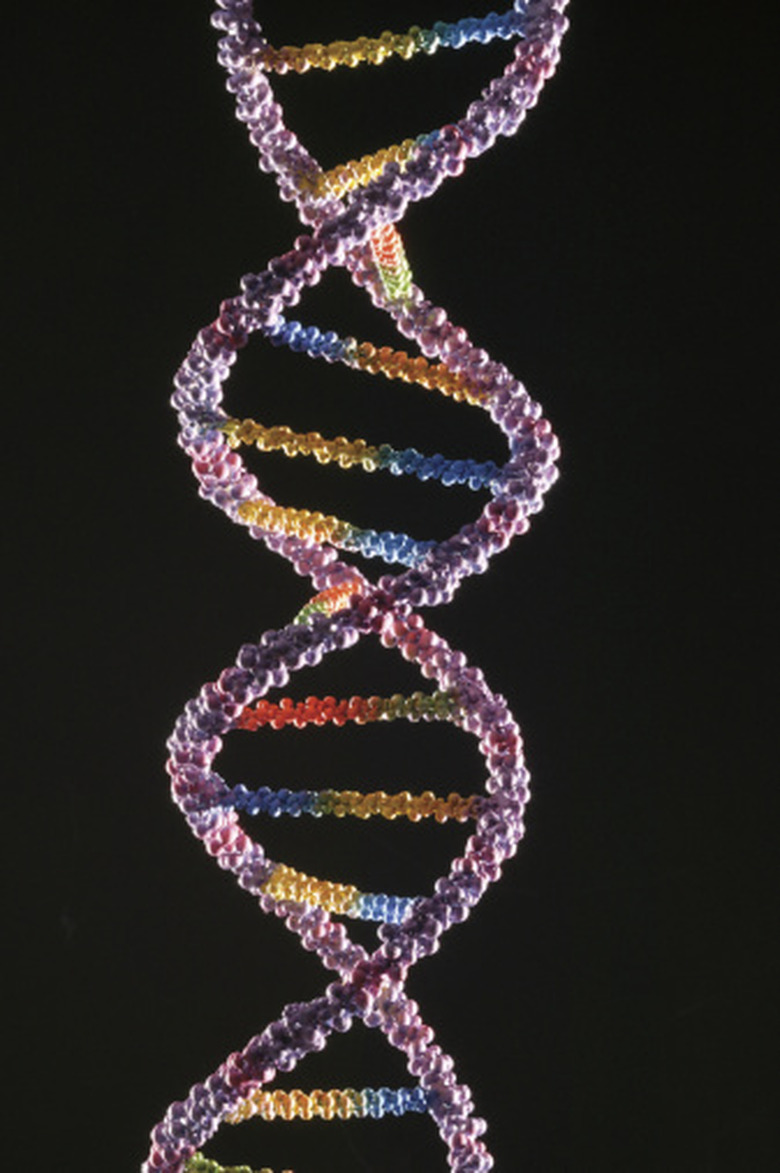
Nucleotides are the subunits of DNA. The four nucleotides are adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. Each of the four bases has three components, a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar and a nitrogen-containing base. The nitrogenous base attached to the bases may be a double-ringed purine or a single-ringed pyrimidine. Adenine and guanine are purine bases, while cytosine and thymine are pyrimidine bases. These four nucleotides, referred to as the A, C, G and T are the building blocks of DNA.
Arrangements of Subunits
Arrangements of Subunits
The four nucleotides join with each other and form what is famously known as the DNA ladder. Hydrogen bonds form only between a purine and a pyrimidine nucleotide base, so the adenine always binds to thymine and cytosine to guanine to form a long chain. Further linking on the DNA ladder occurs by the bonding of the sugar of one nucleotide to the sugar of the adjoining nucleotide by a phosphate group. The sugar phosphate bonding forms the sides of the DNA ladder and is responsible for the twist in DNA.
Human DNA
Human DNA
The Human Genome Project determined the sequence of the three billion bases present in human DNA. The arrangement of these bases encode for the 20,000 different genes present on 23 pairs of chromosomes. The sequence of the bases reveals information that scientists use to diagnose diseases, find cures and even fight crime.
An Interesting Fact
An Interesting Fact
A chain formed by joining the DNA from every cell in the human body can make approximately 70 round trips from the earth to the sun.
Cite This Article
MLA
Ph.D., Sukhsatej Batra,. "What Are The Subunits Of DNA?" sciencing.com, https://www.sciencing.com/subunits-dna-8435779/. 24 April 2017.
APA
Ph.D., Sukhsatej Batra,. (2017, April 24). What Are The Subunits Of DNA?. sciencing.com. Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/subunits-dna-8435779/
Chicago
Ph.D., Sukhsatej Batra,. What Are The Subunits Of DNA? last modified March 24, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/subunits-dna-8435779/